Situational Leadership is a dynamic and adaptive approach to leading that recognizes the need for flexibility in managing teams. Unlike one-size-fits-all leadership models, Situational Leadership emphasizes adjusting leadership styles based on the readiness and development levels of team members. This guide explores the core principles of Situational Leadership, delves into the various leadership styles within the model, and provides insights on how to match these styles to the specific needs of followers. By understanding and applying these concepts, leaders can effectively navigate diverse situations, fostering growth and achieving better outcomes in their teams.
Discover the intricacies of this topic with rosawblog.com
1. Understanding the Core Principles of Situational Leadership
Situational Leadership is grounded in the idea that there is no single “best” way to lead. Instead, effective leadership depends on the context, particularly the maturity and capability of the team members. Developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard, this model advocates for leaders to assess the situation and adjust their approach accordingly. The core principle is adaptability—leaders must be able to shift their style based on the demands of the task and the needs of their followers.
At the heart of Situational Leadership is the concept of “follower readiness,” which is a measure of an individual’s ability and willingness to take on specific tasks. The model suggests that leadership is most effective when leaders tailor their level of directive and supportive behavior to the follower’s readiness level. By doing so, leaders can foster growth, confidence, and competence within their teams.
This approach requires leaders to be highly perceptive and responsive, balancing the need to guide and support with the need to empower and delegate. Understanding these principles is crucial for anyone looking to develop a flexible and responsive leadership style that adapts to the unique challenges of each situation.
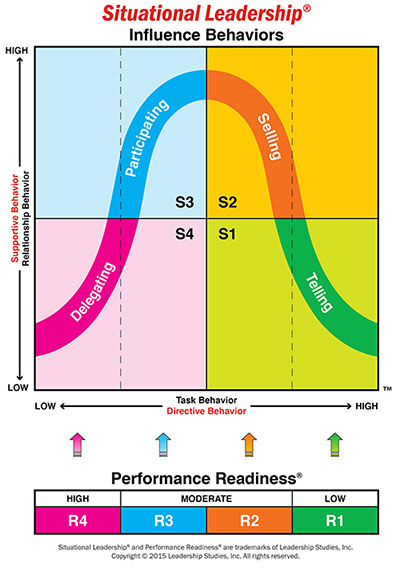
2. Identifying Different Leadership Styles in the Situational Model
The Situational Leadership model identifies four distinct leadership styles, each tailored to different levels of follower readiness and development. These styles are directing, coaching, supporting, and delegating.
Directing: This style is characterized by high levels of directive behavior and low levels of supportive behavior. It is most effective when followers are at a low development level, where they may lack the necessary skills or experience to perform tasks independently. Leaders using this style provide clear instructions and closely monitor progress.
Coaching: In the coaching style, leaders combine high directive behavior with high supportive behavior. This approach is suitable for followers who are willing but still lack the necessary skills. Leaders actively guide followers, offering encouragement while also providing detailed instructions.
Supporting: Here, the leader shifts to high supportive behavior with low directive behavior. This style is ideal for followers who have the skills but may lack confidence. Leaders focus on building morale and motivation, allowing followers to take on more responsibility while offering support as needed.
Delegating: The delegating style involves low levels of both directive and supportive behavior. It is most effective when followers are both competent and confident. Leaders entrust tasks to followers, giving them autonomy to complete the work independently.
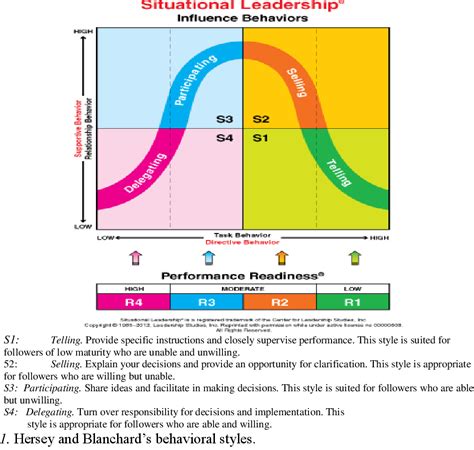
3. Assessing Follower Readiness and Development Levels
Assessing follower readiness and development levels is a crucial step in applying Situational Leadership effectively. Follower readiness refers to an individual’s ability and willingness to perform a specific task. It involves two main components: competence and commitment. Competence is the follower’s skill level and experience related to the task, while commitment reflects their motivation and confidence in carrying it out.
In the Situational Leadership model, followers are categorized into four development levels:
D1: Low competence, high commitment. These followers are enthusiastic but lack the necessary skills.
D2: Some competence, low commitment. Followers have started to develop skills but may be discouraged by challenges.
D3: High competence, variable commitment. These individuals are capable but may lack confidence or motivation.
D4: High competence, high commitment. Followers are both skilled and motivated, ready to work independently.
Leaders must accurately assess where each follower stands in terms of readiness to match their leadership style appropriately. By understanding these development levels, leaders can provide the right balance of direction and support, ensuring that followers grow in competence and confidence, ultimately enhancing team performance and effectiveness.
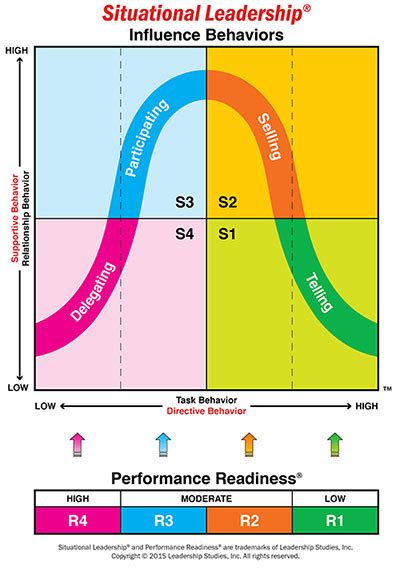
4. Matching Leadership Styles to Follower Needs
Matching leadership styles to follower needs is a pivotal aspect of Situational Leadership. The goal is to align the leader’s approach with the follower’s current development level, ensuring that they receive the appropriate guidance and support to succeed.
For D1 followers (low competence, high commitment), the directing style is most effective. Here, leaders provide clear instructions and closely supervise tasks, helping enthusiastic but inexperienced followers build necessary skills.
For D2 followers (some competence, low commitment), the coaching style is recommended. These followers may feel discouraged as they encounter challenges. Leaders should offer both detailed guidance and emotional support, fostering skill development and renewing commitment.
D3 followers (high competence, variable commitment) benefit from the supporting style. These individuals are capable but may lack confidence or motivation. Leaders should focus on building their confidence, providing encouragement and allowing them more autonomy.
Finally, D4 followers (high competence, high commitment) thrive under the delegating style. These followers are ready to take on tasks independently with minimal supervision. Leaders should trust them to perform, offering autonomy while remaining available for consultation if needed.
By tailoring leadership styles to meet the specific needs of followers, leaders can optimize individual and team performance, fostering growth and success.
5. Adapting Leadership Approaches for Various Situations
Adapting leadership approaches for various situations is at the heart of the Situational Leadership model. Leaders must be agile, continuously assessing and adjusting their styles based on the unique demands of each situation and the evolving needs of their followers.
In dynamic environments, where tasks and challenges frequently change, leaders may need to shift between different leadership styles even within the same team. For example, a leader might use a directing style with a new team member unfamiliar with the job, while simultaneously adopting a delegating style with a seasoned employee who excels in their role.
External factors, such as organizational changes, deadlines, or crises, also influence the choice of leadership style. In high-pressure situations, even skilled and confident followers might require more direction to stay focused and meet urgent objectives. Conversely, during periods of stability, leaders might find it beneficial to step back and delegate more responsibilities, fostering autonomy and innovation among team members.
Leaders must also be mindful of the individual differences within their teams. Some followers may respond better to supportive encouragement, while others might thrive under direct guidance. By staying attuned to these nuances and being willing to adapt their approach, leaders can effectively navigate the complexities of leadership, ensuring that both individual and team needs are met in any given situation.
6. Practical Applications and Examples of Situational Leadership
Situational Leadership is highly practical and can be applied across various industries and scenarios. For instance, in a project management setting, a leader might use the directing style to guide a new team through the initial phases of a complex project, where clear instructions and close supervision are essential. As the team gains experience and confidence, the leader may transition to a coaching or supporting style, offering less direct oversight and more encouragement.
In another example, during a company-wide reorganization, a leader might need to adopt a delegating style with senior managers who are well-versed in their roles and can independently manage their departments. However, for less experienced staff, the leader might shift to a more directive approach to ensure smooth transitions.
By applying the principles of Situational Leadership, leaders can effectively address the specific needs of their teams, fostering a more adaptive and responsive organizational culture. These real-world applications demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of this leadership model in promoting growth, development, and success.
Situational Leadership offers a flexible and effective approach to leadership by emphasizing the need to adapt styles based on follower readiness and situational demands. By understanding and applying the core principles, different leadership styles, and practical applications, leaders can enhance their ability to guide teams successfully. Embracing this model enables leaders to meet diverse challenges, support team development, and drive better outcomes, ultimately fostering a more dynamic and resilient work environment.
rosawblog.com