In today’s educational landscape, emotional intelligence (EI) has emerged as a crucial component in fostering well-rounded students. While traditional education focuses heavily on cognitive skills, the ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions is equally essential for success both in and out of the classroom. Emotional intelligence not only enhances academic performance but also plays a significant role in building strong interpersonal relationships and fostering a positive learning environment. This article explores the concept of emotional intelligence, its importance in education, and practical strategies for cultivating these vital skills in students, empowering them to navigate the complexities of both academic and personal life.
Join rosawblog.com as we uncover the details of this topic.
1. Introduction
The educational landscape is constantly changing, and the significance of cultivating emotional intelligence (EI) in students is becoming increasingly apparent. EI, encompassing the capacity to recognize, comprehend, regulate, and manage emotions, is recognized as a vital aspect of holistic development. Its profound influence on both academic success and overall well-being is being increasingly acknowledged. Historically, education has predominantly focused on intellectual growth, prioritizing cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and knowledge acquisition. However, in an increasingly interconnected and complex world, the ability to navigate emotional terrain—both personal and interpersonal—has become equally vital.
Emotional intelligence (EI) is a crucial element in fostering a positive learning environment where students feel supported, understood, and motivated. It is a key factor in developing essential life skills like empathy, communication, resilience, and conflict resolution. These skills not only contribute to academic success but also prepare students for the social and emotional challenges they will encounter in their personal and professional lives. This article explores the concept of EI, its importance within the educational system, and provides practical strategies for educators to cultivate and enhance EI in their students, resulting in more impactful and meaningful learning experiences.
2. What is Emotional Intelligence?
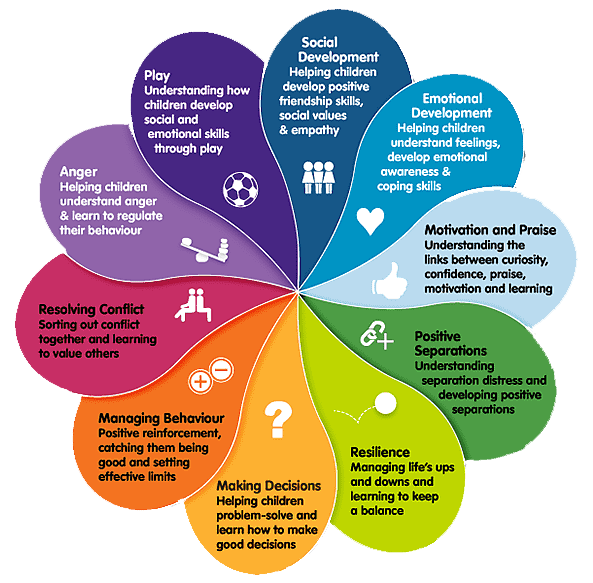
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the capacity to comprehend and manage one’s own emotions, as well as those of others. This multifaceted skill encompasses several crucial components:
* Self-awareness: Understanding one’s own emotions, strengths, and weaknesses.
* Self-regulation: Managing and controlling emotional reactions in various situations.
* Motivation: Possessing the drive to achieve goals with a positive attitude, even when facing challenges.
* Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others, which is fundamental for building strong relationships.
* Social skills: The ability to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and collaborate productively with others.
Emotional intelligence is crucial in education, enabling students to manage their feelings, cultivate positive relationships, and create a nurturing learning atmosphere. By strengthening their EI, students can enhance their academic achievement, improve their social skills, and better equip themselves for the emotional challenges of life.
3. Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Education
Emotional intelligence is becoming increasingly recognized as a crucial element in education, supporting both academic achievement and personal growth. Students with strong emotional intelligence are better prepared to handle stress, maintain motivation, and overcome obstacles—skills that directly influence their learning results. Furthermore, emotional intelligence promotes a positive classroom environment by nurturing empathy, effective communication, and collaboration among students. This not only strengthens peer relationships but also cultivates a more inclusive and supportive learning atmosphere.
Educators recognize the paramount importance of incorporating emotional intelligence into the curriculum to foster well-rounded students. By equipping students with the skills to understand and regulate their emotions, educators empower them to cultivate resilience and a growth mindset. These qualities are essential for overcoming both academic and personal challenges. Furthermore, students who develop strong emotional intelligence are more likely to demonstrate leadership, contribute positively to group dynamics, and navigate complex social interactions effectively, preparing them for success in all aspects of their lives.
4. Strategies to Build Emotional Intelligence in Education
Cultivating emotional intelligence within educational settings necessitates deliberate strategies that seamlessly weave emotional learning into the fabric of daily classroom experiences. A highly effective approach entails integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) programs, meticulously crafted to equip students with the essential skills of self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and adept communication. These programs frequently incorporate engaging activities such as role-playing, interactive group discussions, and introspective reflection exercises, enabling students to effectively identify and navigate their emotional landscape.
Creating a classroom environment that fosters open dialogue and emotional expression is another effective strategy. Educators can model emotional intelligence by demonstrating empathy, engaging in active listening, and responding appropriately to emotions. By cultivating a culture of respect and understanding, teachers can empower students to feel safe expressing their emotions and build stronger interpersonal relationships.
Another powerful tool for enhancing emotional intelligence is to incorporate mindfulness practices into the school day. Mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing and meditation, help students become more aware of their emotions and learn effective strategies for managing stress and anxiety.
In conclusion, educators can cultivate students’ emotional intelligence by incorporating collaborative projects and peer mentoring. These activities allow students to apply their emotional skills in practical settings, fostering their confidence and competency in managing social and emotional difficulties.
5. Case Studies
The positive influence of emotional intelligence on student development and academic success is evidenced by several schools and educational programs that have successfully integrated it into their curricula. One prominent example is a middle school in California that implemented a comprehensive Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) program. Throughout the year, students participated in weekly sessions designed to enhance their self-awareness, emotional regulation, and empathy. These sessions incorporated activities such as journaling, group discussions, and role-playing exercises. Consequently, the school observed a significant decrease in disciplinary issues, alongside an increase in student engagement and academic performance.
A high school in New York successfully implemented mindfulness practices into its daily routine. Teachers initiated brief mindfulness exercises at the start of each class, enabling students to ground themselves and alleviate stress. The school witnessed enhancements in student concentration, emotional management, and overall classroom conduct. Students expressed feeling more tranquil and equipped to handle their academic obligations.
A third instance highlights an elementary school in Texas that prioritized emotional intelligence through peer mentorship programs. In these programs, older students received training to mentor their younger counterparts, emphasizing the development of emotional awareness and interpersonal skills. This initiative not only resulted in heightened emotional intelligence for both mentors and mentees but also cultivated a more robust sense of community within the school. This ultimately contributed to a more positive and supportive learning environment for all.
6. Conclusion
Emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in education, influencing not only academic achievement but also students’ personal development and social abilities. By incorporating emotional intelligence into the curriculum, educators empower students with the skills necessary to regulate their emotions, cultivate strong connections, and navigate the challenges of both academic and personal life. The case studies presented showcase the concrete advantages of cultivating emotional intelligence in educational environments, including improved student conduct, increased concentration, and a more positive school atmosphere.
Emotional intelligence is increasingly recognized as vital. To foster these skills, schools should implement strategies like Social Emotional Learning (SEL) programs, mindfulness practices, and peer mentoring. This will create a more inclusive, supportive, and productive learning environment, ultimately equipping students for success in all areas of their lives.
rosawblog.com